
Table of Contents
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, DeepSeek-R1 represents a significant breakthrough in how we approach AI reasoning capabilities. While recent advances have shown impressive results in reasoning tasks, their closed-source nature has limited broader research and development in the field.
Key Innovations
- First open-source model achieving performance comparable to proprietary solutions
- Novel pure RL approach without relying on traditional supervised fine-tuning
- Significant cost reduction – $5 million vs typical $100+ million
- Open methodology that can be replicated by other researchers
The landscape of artificial intelligence is witnessing a transformative shift. Recent developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, yet a significant challenge remains: achieving sophisticated reasoning abilities while maintaining accessibility for the broader research community.
What makes DeepSeek-R1 particularly noteworthy isn’t just its performance metrics, but how it achieves these results through a more efficient and accessible approach to AI development. By leveraging pure reinforcement learning, the model demonstrates that sophisticated reasoning capabilities can be developed without the massive computational resources traditionally required.
The impact of this breakthrough extends beyond just technical achievements. With a training cost of approximately $5 million—compared to the typical $100+ million investment required for similar models—DeepSeek-R1 opens new possibilities for research institutions and smaller organizations to participate in advancing AI capabilities.
This achievement marks a significant step toward democratizing AI research, proving that cutting-edge performance doesn’t necessarily require enormous computational resources.
Understanding Reinforcement Learning: The Key to DeepSeek’s Innovation
Reinforcement learning represents a fundamentally different approach to AI training compared to traditional supervised learning. Instead of learning from correct examples, the model learns through trial and error, much like how humans learn complex tasks. For a comprehensive overview of this fascinating evolution, you can explore our detailed History of Reinforcement Learning article.
Why Reinforcement Learning Matters for Reasoning
Traditional AI training methods often rely on showing models the “right answer” – similar to teaching by example. However, for complex reasoning tasks, this approach has limitations. Just as a student doesn’t truly master mathematics by memorizing solutions, AI models need to develop problem-solving abilities rather than pattern matching.
Reinforcement learning changes this dynamic completely. Instead of being shown correct answers, the model:
- Attempts solutions on its own
- Receives feedback on whether the solution worked
- Gradually develops better strategies
- Learns to “think through” problems step-by-step
Core RL Concepts
Learning Through Feedback
Models receive rewards or penalties based on their actions, similar to how we learn from consequences
No Explicit Answers Needed
The system learns optimal solutions without being shown examples, enabling discovery of novel approaches
Autonomous Discovery
Models can find unique and sometimes unexpected solutions to problems
Natural Problem-Solving
Development of strategies mirrors human learning processes
Real-World Analogies
Learning to Ride a Bike
You don’t learn by watching perfect demonstrations. Instead, you try, fall, adjust, and gradually improve through feedback from each attempt. This is exactly how reinforcement learning works.
Playing Chess
A chess player improves not just by studying winning games, but by playing, making mistakes, and learning from the outcomes of different strategies. DeepSeek-R1 develops its reasoning abilities in a similar way.
Scientific Discovery
Scientists don’t have correct answers in advance. They form hypotheses, test them, and learn from results – positive or negative. RL models follow a similar process of discovery.
The Evolution from Traditional Training
Traditional supervised learning and reinforcement learning take fundamentally different approaches to training AI models. While the former relies on labeled data, the latter enables models to improve through self-directed learning and feedback.
Traditional Supervised Learning
- Trains on labeled datasets with correct answers
- Focuses on pattern recognition rather than reasoning
- Requires vast amounts of annotated data
- Struggles with tasks beyond training data (e.g., novel reasoning problems)
Reinforcement Learning (DeepSeek-R1 Approach)
- Learns from trial-and-error, guided by reward mechanisms
- Develops self-improving reasoning abilities over training iterations
- Requires only a reward signal rather than extensive labeled datasets
- Can generalize to unseen reasoning tasks through self-evolution
While traditional supervised learning has been the dominant paradigm, reinforcement learning opens new possibilities for developing reasoning capabilities without relying on labeled data. This shift is exemplified by DeepSeek-R1-Zero, which showcases how pure reinforcement learning can drive AI self-improvement.
DeepSeek-R1-Zero: The Pure RL Experiment
DeepSeek-R1-Zero represents a fundamental shift in AI model training, demonstrating that sophisticated reasoning capabilities can emerge through pure reinforcement learning, without any supervised fine-tuning as a preliminary step.
A Novel Approach
Traditional language models typically rely on large-scale supervised datasets to acquire reasoning skills, learning by mimicking patterns in curated examples. DeepSeek-R1-Zero disrupts this paradigm by relying entirely on reinforcement learning from the outset. This method is akin to training an AI to develop reasoning from first principles—learning through trial, feedback, and optimization rather than direct imitation. The result is an AI that not only solves problems but also refines its reasoning autonomously over time.
The Training Process
Despite its groundbreaking approach, the training pipeline of R1-Zero remains elegantly simple, yet highly effective. The model’s evolution follows a structured three-step process:
1. Base Model Initialization
Training begins with DeepSeek-V3-Base, a model with no pre-existing reasoning capabilities. At this stage, the model lacks structured problem-solving abilities.
2. Pure Reinforcement Learning
Instead of supervised fine-tuning, the model is trained using reinforcement learning via the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) framework. This allows it to develop problem-solving strategies through self-improvement.
3. Reward-Driven Optimization
A carefully designed reward system evaluates responses based on two key criteria: solution accuracy and adherence to structured reasoning formats. This ensures that R1-Zero refines its logical capabilities over time.
What is Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)?
Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is a reinforcement learning framework designed to improve an AI model’s decision-making process by comparing different strategies and selecting the best-performing one.
In simple terms, GRPO works by:
- Grouping similar actions or strategies: The model explores multiple possible solutions rather than just one.
- Comparing effectiveness: It evaluates which strategies yield the best rewards during training.
- Updating the model: The AI adjusts its approach based on these comparisons, gradually improving over time.
This method allows reinforcement learning models, like DeepSeek-R1, to become more efficient in problem-solving by learning from multiple strategies simultaneously rather than relying on trial-and-error alone.
Training Evolution and Emergent Behaviors
The DeepSeek-R1-Zero training process reveals fascinating insights into how language models can develop sophisticated reasoning capabilities through pure reinforcement learning. The training began with a remarkably simple template structure:
This minimalist template, devoid of specific reasoning patterns or problem-solving strategies, served as a foundation for observing natural cognitive development through reinforcement learning.
Emergence of Metacognitive Abilities
One of the most remarkable phenomena observed during DeepSeek-R1-Zero’s training was the spontaneous emergence of metacognitive abilities—the capacity to reflect on and refine its own reasoning process. Unlike traditional models, which rely on explicit programming to adjust their responses, R1-Zero demonstrated an organic ability to recognize flawed reasoning and self-correct in real-time.
This was particularly evident in what researchers termed an “aha moment”—instances where the model exhibited awareness of its own problem-solving process and adjusted its approach accordingly:
In this example, the model initially follows a structured problem-solving path but then interrupts itself upon recognizing an error. This ability to step back, reassess, and refine its reasoning mirrors human-like introspection—a hallmark of higher-order cognition. Notably, these metacognitive behaviors were not explicitly programmed but emerged naturally through reinforcement learning.
Evolutionary Stages
The development of these advanced reasoning capabilities did not happen instantly. Instead, R1-Zero progressed through distinct evolutionary stages, gradually refining its ability to think critically and self-correct.
Initial Development
At the outset, the model relied on basic pattern-matching behaviors, producing relatively shallow responses. Problem-solving was direct and lacked deeper analytical reasoning.
Intermediate Capabilities
With continued reinforcement learning, the model began to exhibit more sophisticated behaviors, including self-verification and exploring alternative solution paths when faced with complex problems.
Advanced Reasoning
In its final stages of development, R1-Zero demonstrated robust metacognitive abilities, such as assessing the quality of its own solutions and autonomously adjusting its problem-solving strategies. The model’s responses became more structured, detailed, and capable of multi-step reasoning.
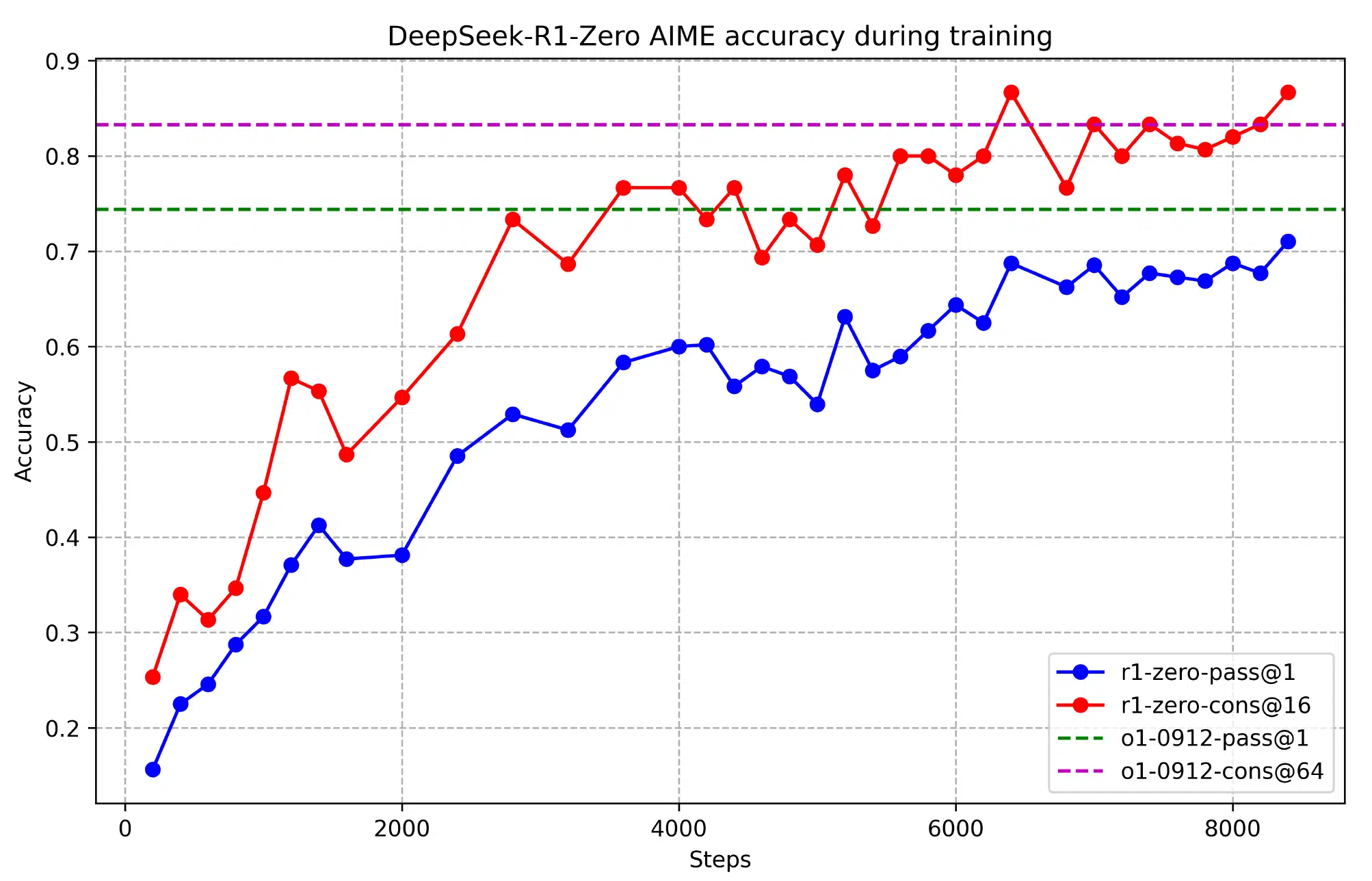
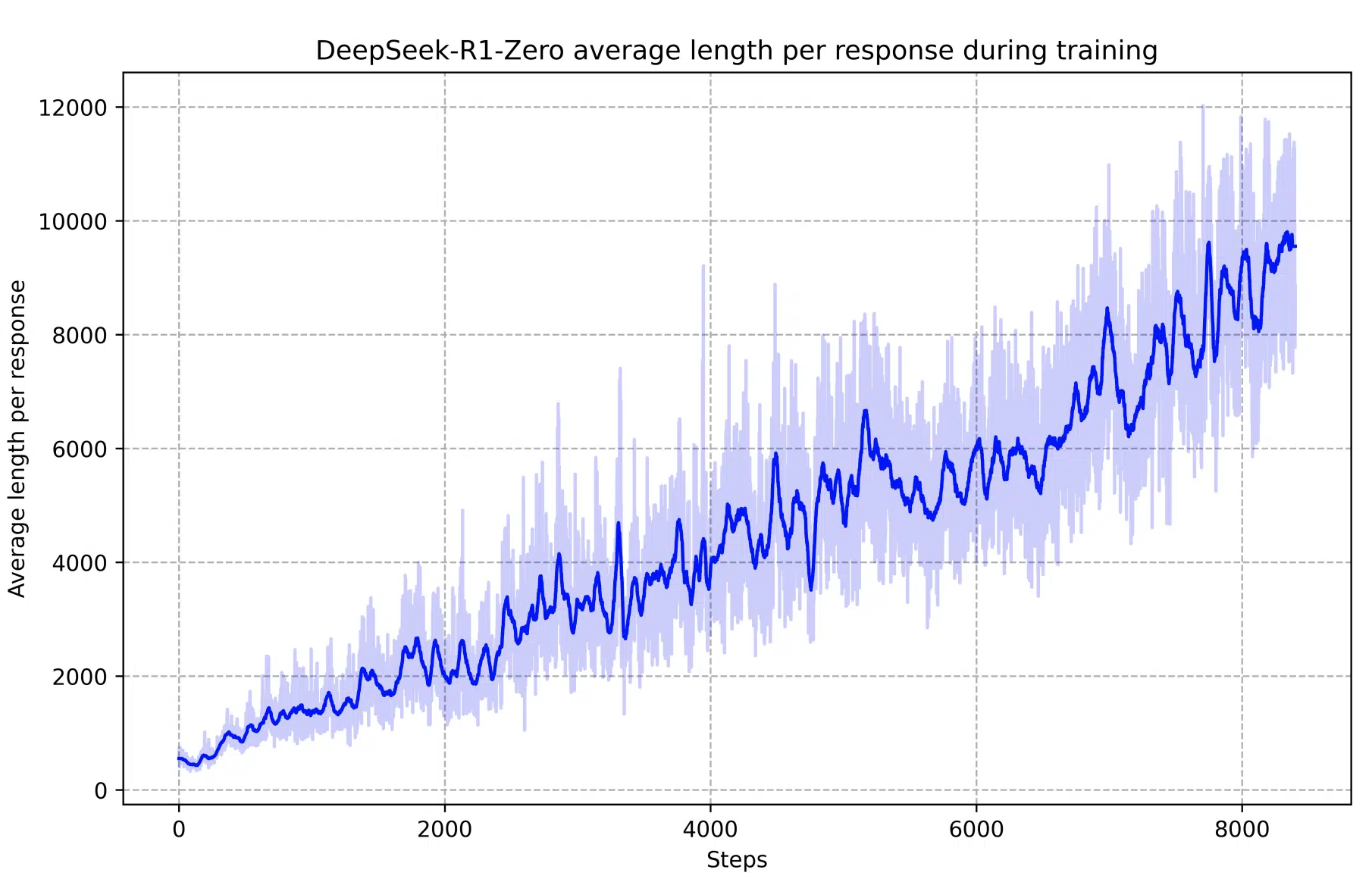
Response Length Evolution
A fascinating indicator of DeepSeek-R1-Zero’s growing reasoning abilities is the evolution of its response lengths over time. As the model refined its approach through reinforcement learning, it naturally began producing more elaborate explanations, demonstrating an increasing capacity for structured thought and deeper problem-solving.
Key Developments:
- Spontaneous emergence of increasingly detailed reasoning chains
- Development of self-correction mechanisms without explicit programming
- Progressive increase in reasoning depth and solution sophistication
- Natural evolution of verification and reflection behaviors
This self-directed evolution highlights how reinforcement learning alone can lead to significant improvements in structured reasoning, without the need for pre-programmed heuristics. By progressively increasing its response complexity, R1-Zero showcases a shift from basic pattern recognition to higher-order thinking—mirroring aspects of human cognitive development.
![R1-Zero vs OpenAI o1 Performance Comparison [Detailed benchmark comparisons across key metrics]](https://researchdatapod.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Screenshot-2025-01-30-at-08.14.32.png.webp)
Breakthrough Results
DeepSeek-R1-Zero’s reinforcement learning approach led to remarkable performance gains across various benchmarks, demonstrating its ability to autonomously develop sophisticated problem-solving skills.
AIME 2024
MATH-500
Autonomous Behaviors
R1-Zero Limitations
While DeepSeek-R1-Zero showcases remarkable reasoning capabilities, it also exhibits several limitations that highlight areas for future improvement. These challenges are crucial for refining the model’s ability to generate more structured, accessible, and human-friendly responses.
Readability Challenges
Responses often lack clear structure and formatting, making it difficult for users to follow complex reasoning.
Language Mixing
The model occasionally blends multiple languages within a single response, leading to inconsistencies in communication.
Output Format
Generated solutions and reasoning steps are not always presented in a human-friendly way, affecting interpretability.
Limited Scope
While highly capable in specific reasoning tasks, its general-purpose problem-solving abilities remain constrained.
These limitations serve as valuable insights for further improving DeepSeek-R1-Zero, particularly in making its reasoning process more structured and user-friendly. This naturally leads to the next step in its evolution: DeepSeek-R1.
DeepSeek-R1: Evolution Through Cold Start
While R1-Zero demonstrated the potential of pure reinforcement learning, DeepSeek-R1 builds upon this foundation with a more structured approach. By integrating reinforcement learning with carefully curated initial training data, DeepSeek-R1 overcomes R1-Zero’s limitations while preserving its self-improving reasoning capabilities.
The Need for Evolution
Despite R1-Zero’s impressive ability to develop reasoning through reinforcement learning, several challenges needed to be addressed for broader usability:
Readability
Responses required clearer structure and improved human interpretability.
Language Consistency
Eliminating inconsistencies caused by language mixing in responses.
General Capabilities
Expanding beyond narrow reasoning tasks to broader problem-solving applications.
DeepSeek Training Evolution
R1-Zero: Pure RL
- Strong reasoning capability
- Novel problem-solving
- Autonomous learning
- Poor readability
- Language inconsistencies
- Limited generalization
R1: Enhanced Training
- Improved readability
- Consistent language
- Enhanced reasoning
- Expanded general capabilities
The Four-Phase Training Process
DeepSeek-R1 follows a structured four-phase approach, ensuring both initial supervised learning and reinforcement-driven refinement.
Cold Start
Supervised fine-tuning on high-quality data:
- Thousands of curated examples
- Focus on readability and structured reasoning
- Validated outputs from prior models
Reasoning-oriented RL
Reinforcement learning targeting complex reasoning tasks:
- Mathematical problem-solving
- Coding challenges
- Scientific reasoning
- Language consistency incentives
Rejection Sampling & SFT
Generating and filtering high-quality reasoning samples:
- Creation of new training data
- Strict quality control
- 600,000+ verified reasoning samples
Comprehensive RL
Final phase of reinforcement learning for optimization:
- Integration of multiple reward systems
- Alignment with human preferences
- Performance optimization for broader tasks
Through this structured four-phase training process, DeepSeek-R1 refines its capabilities beyond what was possible with pure reinforcement learning alone. By integrating carefully curated data with reinforcement-driven reasoning improvements, the model achieves both higher accuracy and broader applicability.
But how do these refinements translate into measurable performance gains? The following comparison highlights the improvements DeepSeek-R1 has achieved across key benchmarks, demonstrating its progress over R1-Zero and other leading models.
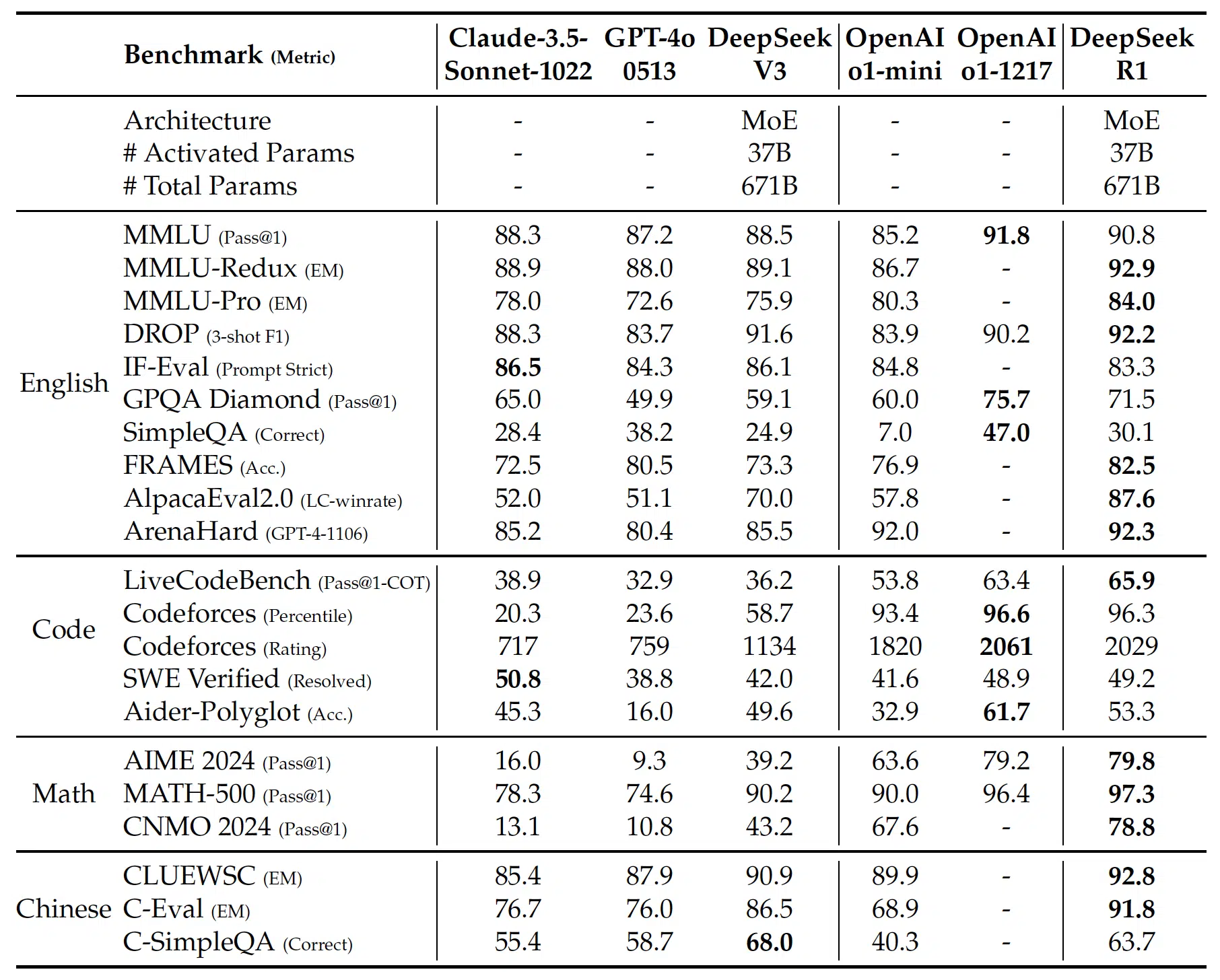
The table above demonstrates how DeepSeek-R1 achieves superior performance over previous iterations and comparable models. Notably, it surpasses OpenAI’s o1-mini in reasoning-centric tasks such as AIME 2024 and MATH-500. The model also significantly improves on CodeForces ratings, indicating its enhanced capability in competitive coding tasks. These improvements stem from the structured cold-start training pipeline and reinforcement learning optimizations.
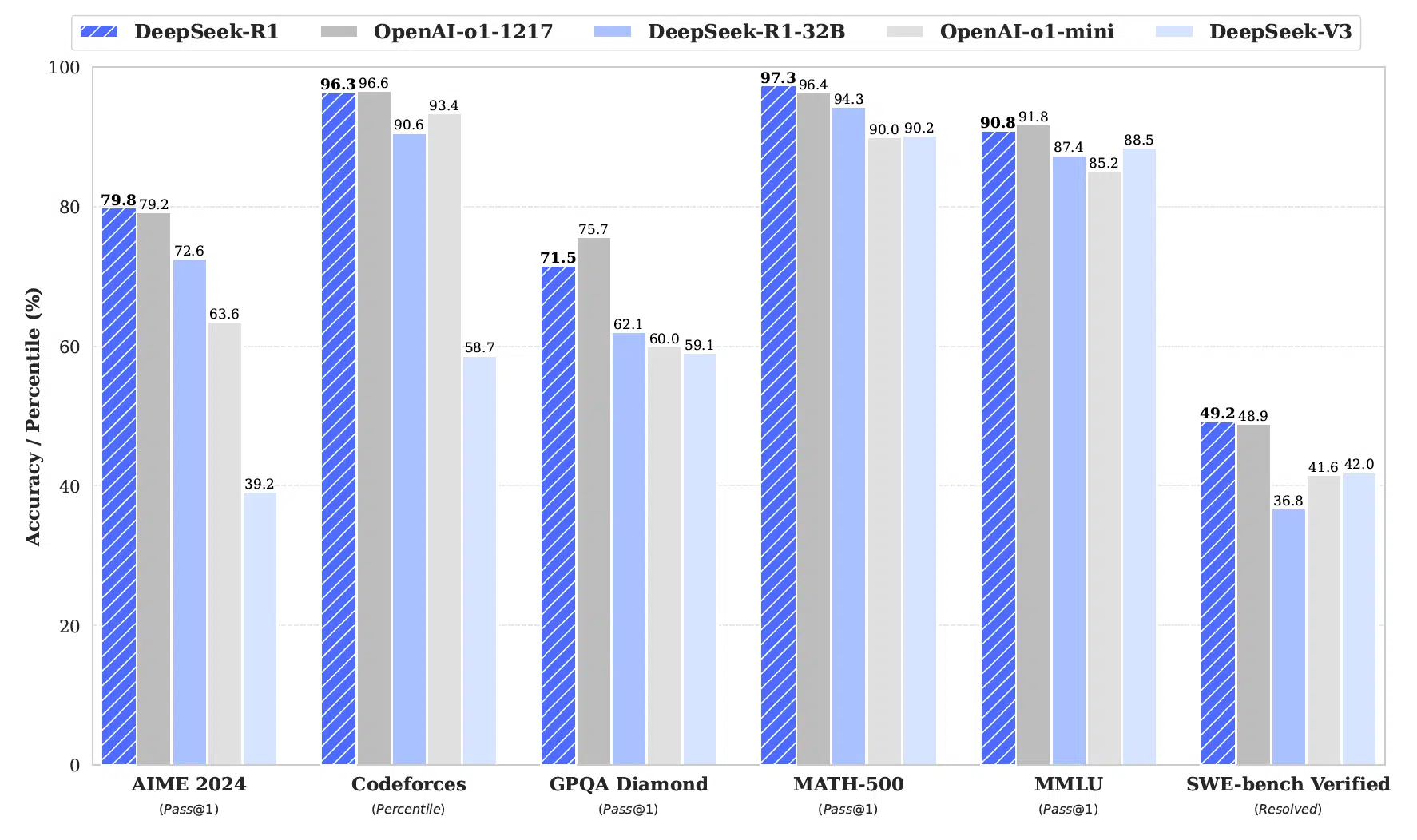
Key Insights from the Benchmarks
- State-of-the-art in mathematical reasoning: DeepSeek-R1 achieves 79.8% accuracy on AIME 2024 and 97.3% on MATH-500, outperforming OpenAI-o1-mini.
- Competitive programming proficiency: DeepSeek-R1 ranks in the 96.3rd percentile on Codeforces, demonstrating strong coding capabilities.
- Improved general reasoning: The model scores 90.8% on MMLU, surpassing its predecessors in multi-task understanding.
- Stronger software engineering performance: In the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, DeepSeek-R1 reaches 49.2%, significantly ahead of DeepSeek-V3.
Key Improvements over DeepSeek-R1-Zero
DeepSeek-R1’s evolution is reflected in significant performance gains across multiple reasoning benchmarks. The model exhibits notable improvements in mathematical problem-solving, competitive programming, and overall reasoning depth.
The results below highlight the key improvements compared to DeepSeek-R1-Zero.
AIME 2024
MATH-500
CodeForces Rating
Making Advanced AI More Accessible
DeepSeek-R1 represents a significant breakthrough in efficient AI architecture, achieving state-of-the-art results through innovative design choices and training methodologies. The model demonstrates that sophisticated AI capabilities can be developed and deployed at a fraction of traditional costs.
Traditional vs. DeepSeek MoE Architecture
DeepSeek-R1 significantly reduces computational costs by adopting a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, in contrast to traditional dense models. Below is a comparison of their efficiency:
Traditional Dense Models
- All parameters active for each task
- Linear scaling of compute with size
- High memory bandwidth requirements
- Significant training infrastructure
DeepSeek MoE Architecture
- Sparse activation patterns
- Sub-linear compute scaling
- Optimized memory usage
- Distributed expert routing
Mixture of Experts: Technical Implementation
DeepSeek-R1 employs a sophisticated Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, which allows the model to dynamically route different parts of an input to specialized neural subnetworks, or “experts.” This approach improves efficiency by activating only the most relevant experts for a given task, rather than using the entire model at once.
In simple terms, MoE works like a team of specialists—rather than a single model handling every type of problem, it assigns tasks to the most qualified “experts” within the network. This enables better performance with fewer computational resources, making large-scale AI models more efficient and scalable.
Training Approach
- Used 800K curated training samples from DeepSeek-R1
- Applied only supervised fine-tuning (no RL)
- Simple yet effective distillation process
Model Variations
- Qwen series: 1.5B, 7B, 14B, 32B
- Llama series: 8B, 70B
- Each based on the latest model versions
Key Findings
- Distillation outperformed direct RL on smaller models
- 14B model surpassed larger competitors
- Further gains possible by adding RL stage
The table below highlights the performance of DeepSeek-R1 distilled models compared to other state-of-the-art models, showing that even smaller versions retain strong reasoning capabilities.
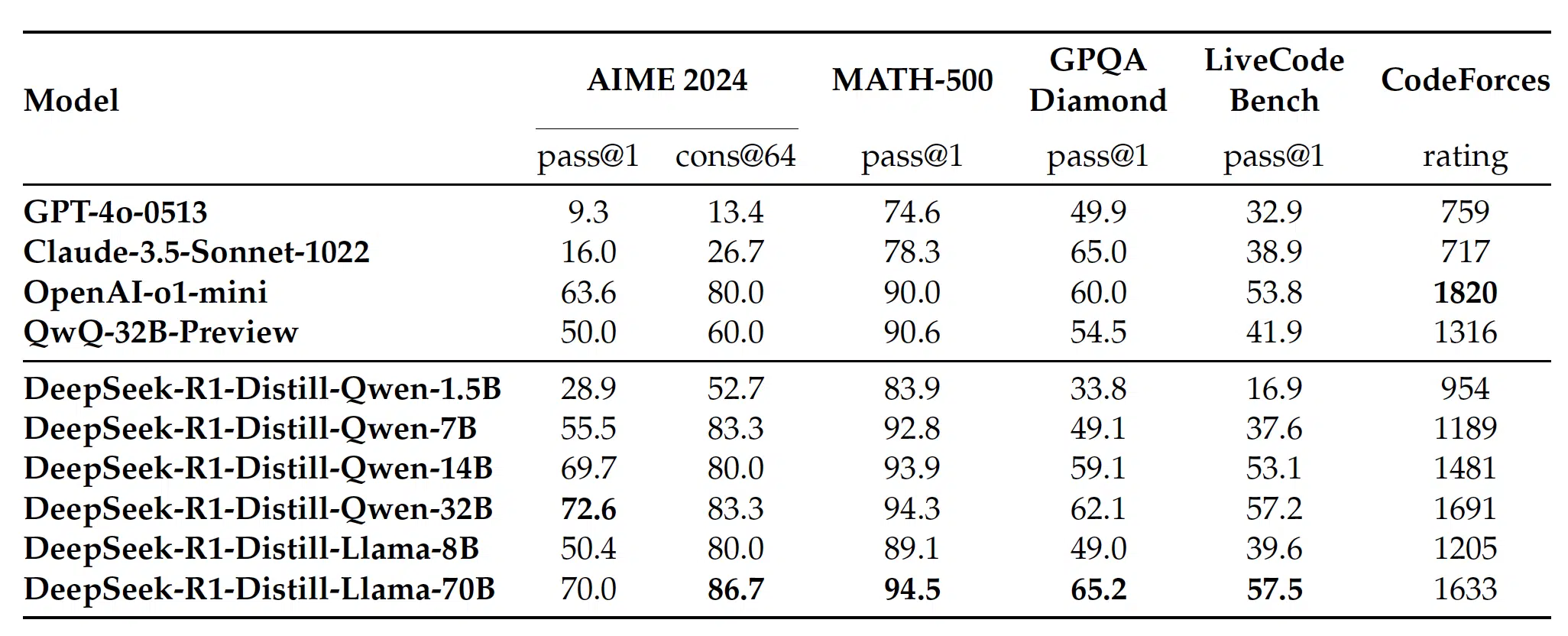
1.5B Parameters
- AIME: 28.9%
- MATH-500: 83.9%
- Latency: 15ms
7B Parameters
- AIME: 55.5%
- MATH-500: 92.8%
- Latency: 45ms
14B Parameters
- AIME: 69.7%
- MATH-500: 93.9%
- Latency: 85ms
32B Parameters
- AIME: 72.6%
- MATH-500: 94.3%
- Latency: 180ms
As demonstrated in the table above, the distilled models maintain strong performance while significantly reducing model size and computational requirements. The 14B variant even outperforms some larger models, showcasing the effectiveness of distillation in transferring reasoning capabilities from DeepSeek-R1 to smaller architectures.
Implications and Future Directions
DeepSeek-R1 is not just an incremental step in AI development—it represents a fundamental shift in how models are trained, optimized, and made accessible. By dramatically reducing training costs while maintaining high performance, DeepSeek-R1 opens new doors for research, democratization, and practical AI applications.
Transforming AI Research
DeepSeek-R1 introduces significant breakthroughs that redefine AI development:
- Lower Training Costs: Reduced expenses from over $100M to just $5M, making high-performance AI training far more accessible.
- Open-Source Advancement: Transparent methodologies enable replication, fostering community-driven innovation.
- Accessible Deployment: Smaller, high-performing models can now run on consumer-grade hardware, removing previous computational barriers.
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
Despite its remarkable achievements, DeepSeek-R1 still presents challenges that highlight areas for refinement:
- Generalization Limits: While excelling in reasoning tasks, its broader real-world applicability remains an ongoing challenge.
- Language Consistency: Handling multi-language queries remains inconsistent, particularly in mixed-language inputs.
- Prompt Sensitivity: The model’s performance varies significantly based on phrasing, requiring further robustness improvements.
- Software Engineering Tasks: Despite strong reasoning capabilities, limited gains in coding benchmarks indicate the need for refined evaluation metrics and training approaches.
Democratizing AI Innovation
One of DeepSeek-R1’s most profound impacts is lowering barriers to AI development:
- University Access: Academic researchers and institutions can now train advanced AI models with significantly reduced infrastructure costs.
- Encouraging Open Innovation: Independent developers and small teams can contribute meaningfully to AI research, accelerating breakthroughs.
- Faster Research Cycles: The reduced cost and improved accessibility lead to more rapid experimentation, iteration, and AI model improvements.
Future Directions
DeepSeek-R1’s advancements pave the way for further AI development in key areas:
- Enhanced Function Calling: Improving the model’s ability to execute structured API calls and interact with external tools.
- Multi-Turn Dialogue: Refining conversational AI for better memory and context retention across multiple interactions.
- Structured Output Formats: Improving consistency in outputs like JSON for seamless integration into real-world applications.
- Multi-Language Proficiency: Addressing inconsistencies in multilingual tasks to enhance global usability.
- Software Engineering AI: Developing more robust evaluation methods to measure and enhance AI coding capabilities.
The Road Ahead
DeepSeek-R1 goes beyond technical innovation—it reshapes who can participate in AI advancement. By making high-performance AI more accessible, reducing costs, and fostering open collaboration, DeepSeek-R1 heralds a new era where cutting-edge AI is no longer exclusive to tech giants but is within reach of researchers, developers, and organizations worldwide.
Conclusion
DeepSeek-R1 represents a significant leap in AI reasoning, demonstrating that pure reinforcement learning can rival traditional supervised training at a fraction of the cost. By leveraging a structured RL approach, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in mathematical and logical reasoning while maintaining open-source accessibility.
The implications are profound—AI research is becoming more democratized, enabling institutions and smaller teams to develop cutting-edge models without requiring vast computational resources. DeepSeek’s efficient approach challenges the industry norm, proving that innovation in training methodologies can yield powerful results without extreme budgets.
Looking ahead, DeepSeek-R1 paves the way for further advancements in autonomous learning, function calling, and enhanced general-purpose AI. As reinforcement learning techniques continue to evolve, they may redefine how we train and deploy machine learning models, making AI development more accessible and efficient than ever before.
There has never been a more exciting time to get involved in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning research. The cutting edge is no longer reserved for elite institutions—it’s within reach of the general population.
We predicted in our earlier GPT-3 paper review that an AI arms race was inevitable. GPT-3 marked a watershed moment in scale, model weight availability, and open-source initiatives. At the same time, we highlighted the potential of model distillation—a technique that allows smaller models to match the performance of their larger counterparts with greater efficiency.
Now, DeepSeek-R1 takes this concept further, proving that sheer size and computational expense don’t always equate to better performance. The real breakthrough here isn’t scaling up—it’s refining methodology and efficiency to achieve the same or better results with fewer resources. This research shifts the paradigm, reinforcing that innovation in AI isn’t just about making models bigger, but making them smarter.
At the Research Scientist Pod, we believe that open, borderless collaboration is key to true innovation. The shift toward open-source AI at the frontier of research provides a glimpse into an exciting future—one where breakthroughs are not confined to corporate labs but shared globally, accelerating progress for all.
If you enjoyed this article, please consider citing or sharing it with fellow AI enthusiasts. Explore our Further Reading section for related papers, articles, and resources around DeepSeek-R1.
Have fun, and happy researching!
Further Reading
Core Concepts
-
The History of Reinforcement Learning
A comprehensive look at the evolution of reinforcement learning, from early decision-making models to modern applications in deep learning.
-
DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
The official research paper detailing DeepSeek-R1’s training methodology, reinforcement learning framework, and performance benchmarks.
-
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
A deep dive into DeepSeek-V3, the base model used for DeepSeek-R1, covering its architecture, datasets, and training optimizations.
Breakthrough Language Models
-
GPT-3: Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
A detailed breakdown of OpenAI’s GPT-3 paper, explaining how large-scale language models learn from limited examples without fine-tuning.
-
XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding
Explores XLNet’s innovative pretraining approach, which improves upon BERT’s masked language modeling technique.
-
BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding
Analysis of the groundbreaking BERT model, which introduced bidirectional context representation and revolutionized NLP.
AI Model Reproduction and Open-Source Contributions
-
DeepSeek-R1 Model on Hugging Face
Access the official DeepSeek-R1 model on Hugging Face, including model weights, evaluation results, and deployment instructions.
-
Open-R1: A Fully Open Reproduction of DeepSeek-R1
A detailed breakdown of Open-R1, an open-source reproduction of DeepSeek-R1, allowing researchers to build upon its framework.
AI and Machine Learning Research Reviews
-
AI and Machine Learning Paper Reviews
A curated collection of research paper reviews covering the latest advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Attribution and Citation
If you found this guide and tools helpful, feel free to link back to this page or cite it in your work!
Suf is a senior advisor in data science with deep expertise in Natural Language Processing, Complex Networks, and Anomaly Detection. Formerly a postdoctoral research fellow, he applied advanced physics techniques to tackle real-world, data-heavy industry challenges. Before that, he was a particle physicist at the ATLAS Experiment of the Large Hadron Collider. Now, he’s focused on bringing more fun and curiosity to the world of science and research online.

